
Software Development Use Cases
Unlock the secrets to successful software development with this carefully curated selection of real-world use cases.
In this collection you’ll learn
- How to identify and address software process bottlenecks effectively.
- Tips to improve collaboration and communication in development teams.
- Ways to manage software projects for timely delivery.
- How to implement agile methodologies and optimize workflow.
- How to solve software engineering problems, including debugging, testing, and refactoring.
- How to prioritize tech debt.
- … and much more.
ARTICLES IN THIS COLLECTION
Software Development Use Cases
- How to Deliver with Constant Pivots
- Permission Management with CASL
- How to Use Software Metrics
- How to Use Metrics to Increase Your Team’s Performance
- When Monolith Is Better Than Microservices
- How to Run an Expectation Workshop
- Enhanced Type Safety with Zod
- Bitrise to GitHub Actions Migration Study
Practical insights from software development use cases
In this handbook, you’ll find a diverse set of use cases connected to software development.
Learn directly from the hands-on challenges others faced, understanding the strategies that led to breakthrough solutions. By analyzing these scenarios, you’ll arm yourself with a toolkit of problem-solving approaches.
Pick a use case from the list on the right or scroll down to learn some details first.
How to deliver with constant pivots and changes in team composition
This use case discusses strategies for maintaining project momentum and delivery in environments characterized by frequent shifts and changes in team dynamics. It provides insight into how the Kanban system facilitates agility and adaptability in project management.
The problem: Constant changes and pivots
The problem tackled is the inefficiency and resource waste that occur when teams face frequent pivots and alterations in team composition without a clear process to manage these changes.
Kanban as a solution
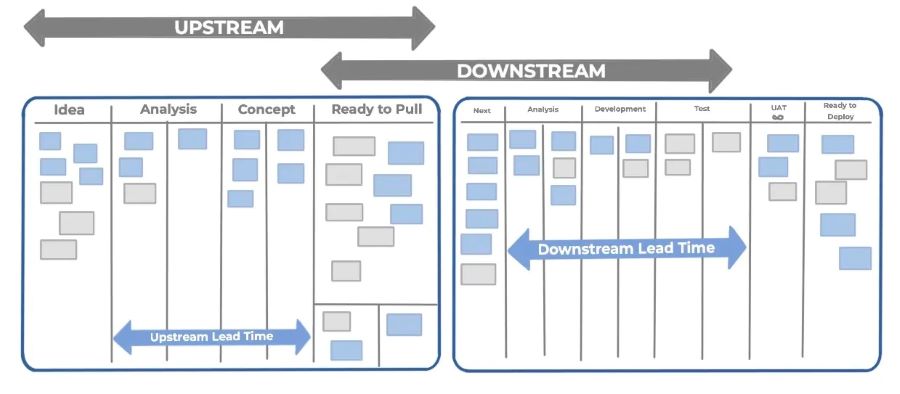
The implementation of a Kanban framework, specifically the upstream-downstream approach, helps to manage tasks effectively.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- The structure and advantages of using an upstream-downstream Kanban system.
- How to implement Kanban in your project management practices.
- Methods for refining tasks to ensure a smooth transition from idea to execution.
- Strategies for improving planning accuracy and efficiency in project management.
Granular permission management with CASL library
The use case delves into how the CASL library can enhance permission management in web applications, addressing the common challenges associated with complex access control requirements.
The problem: Managing user permissions in multifaceted applications
The problem tackled is the difficulty of managing user permissions in multifaceted applications, particularly when dealing with a variety of user roles that require access to certain data, a problem that escalates as the application and roles evolve.
CASL as a solution
CASL (an acronym for “Create, Read, Update, Delete”) is a JavaScript library that allows for defining detailed user permissions aligned with their roles, streamlining the process of who can see and do what within the application.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- How CASL was used in a Metrics Tool application to define and enforce user roles and permissions.
- The complexities of permission management in large-scale applications.
- How to implement the CASL library for managing permissions in JavaScript applications.
- The benefits of using a granular approach to permission management.
- The ways in which precise permission control can lead to better security and more informed decision-making within IT project management tools.
How to use metrics to increase your team’s performance
The use case provides guidance on enhancing team performance through effective use of metrics, warning against the pitfalls of misusing them as targets.
The problem: Real change of behavior
The article confronts the issue that simply setting targets on metrics does not necessarily change behavior, as individuals might manipulate the system to meet these targets without genuine performance improvements.
Four golden rules of using metrics
Like an EKG, metrics should be used to diagnose issues and inform strategies for improvement rather than to set direct targets for teams.
Effective metric usage involves four golden rules: not relying on a single metric, keeping metrics objective, measuring only what’s worth measuring, and recognizing that there is no universal set of metrics.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- Why metrics should not be used as direct targets.
- Strategies for selecting and interpreting metrics effectively.
- How to apply metrics to diagnose and improve team performance.
- Ways to familiarize yourself with metrics to make informed decisions and implement meaningful changes.
Don’t believe the hype: Sometimes a monolith is better than microservices
The use case discusses the debate between microservices and monolithic architectures, especially for smaller projects, and provides insights into why sometimes a monolithic structure might be more beneficial.
Key issue: scalability vs complexity of the architecture
Choosing between microservices and a monolithic architecture affects development complexity and speed. While microservices are scalable, they introduce complexity and slow initial development, whereas monolithic architecture, although less scalable, can be quicker and simpler for smaller projects.
Modular monolith can be a solution

Adopting a modular monolithic approach can be effective for certain projects. This method allows for easy separation into logical modules and the ability to shift to microservices later if necessary.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- When and why a monolithic architecture might be preferable to microservices.
- Factors to consider before deciding on the project’s architectural design.
- How to validate for choosing a simpler, more traditional architecture amidst the microservices hype.
How to run an Expectation Workshop and reduce project conflicts
This use case presents an Expectation Workshop as an essential tool to address the common issue of delays and frustrations in software projects caused by mismatched expectations among stakeholders and developers.
The problem: Mismatched expectations
The use case tackles the challenge of misunderstandings, rework, and missed deadlines in software development, exacerbated by differences in backgrounds and communication styles in multicultural teams.
Expectation Workshop as a solution
The solution involves conducting an Expectation Workshop that encompasses 8 key steps. In the example presented by the use case, Expectation Workshop allows the team to capture information asymmetry and validated false beliefs, which led to process improvements, faster delivery of higher quality work, and greater team satisfaction.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- How to effectively organize and run an Expectation Workshop.
- Strategies for enhancing communication and reducing misunderstandings in software projects.
- Methods for managing multicultural teams and diverse communication styles.
- Ways to identify and correct information asymmetry within a team.
Enhanced type safety with Zod – Tame badly typed external libraries
This use case demonstrates how Zod, a robust validation library, was pivotal in resolving integration issues stemming from the poorly typed code in the AdminJS library.
The problem: Poorly typed code causing integration complexities
The use case focuses on the difficulties encountered with AdminJS’s inadequately typed code, which led to integration complexities and the potential for runtime errors.
Using Zod library as a solution
Zod was leveraged to define precise type schemas and perform data validation against these schemas, which facilitated early error detection during development and bolstered overall code quality.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- Strategies for ensuring type safety when integrating external libraries with weakly typed code.
- How to create comprehensive type definitions and validations using Zod.
- Techniques for refining schemas and modifying values after validation.
- The utility of creating subschemas for handling different parts of data payloads.
- The application of type guards to maintain robustness in dynamically typed environments.
Automating mobile CI/CD: Bitrise vs GitHub Actions + Migration study
This use case delves into the strategic migration from Bitrise to GitHub Actions for a more streamlined CI/CD process.
The problem: Scaling with Bitrise
The use case addresses the challenges of scaling up mobile application development processes with Bitrise and the need for a more flexible, cost-effective solution.
Migration to GitHub Actions

The solution involves transitioning to GitHub Actions, which offers greater control over CI/CD pipelines and integrates more seamlessly with GitHub repositories, as detailed in the study.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- Practical aspects of migrating CI/CD processes
- How GitHub Actions can potentially offer better performance than Bitrise
- Considerations for workflow optimization during platform migration
- Technical and strategic benefits of using GitHub Actions for mobile app CI/CD
Solving the tech debt puzzle: Strategies that boost business
This use case addresses the complexities and challenges of managing technical debt in a legacy software system that suffers from poor code quality, scalability issues, and insufficient testing and documentation.
The problem: accumulating tech debt

The use case presents the challenges that technical debt poses to maintaining and scaling software systems effectively. Additional challenge was the selection of the right approach and debt prioritization.
Strategic approach as a solution
The solution involves a strategic approach to technical debt, assessing its impact, and integrating its management into the daily workflow. The team used a tech audit to prioritize issues, aligning refactoring with business goals, adopting the Testing Trophy strategy over traditional testing pyramids, and taking incremental steps in refactoring with a focus on business value and strategic improvement
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- How to conduct a tech audit and its significance in addressing tech debt.
- The importance of prioritizing technical tasks based on potential business impact.
- Alternative testing strategies that might be more beneficial than traditional methods in some scenarios.
- Strategies for refactoring legacy systems incrementally to align with business objectives.
- The value of modular development and event-driven architecture in isolating and addressing technical debt.
PDF insights with AWS Textract and OpenAI integration
This use case details a method for efficiently extracting information from PDF pitchdecks, tackling the difficulties of handling unstructured data and graphical elements.
The problem: extracting unstructured data from PDFs
The problem was the extraction of pertinent information from a large volume of pitchdecks in PDF format, which are typically unstructured and feature a mix of text, images, and spatial relationships that standard text extraction tools struggle to interpret.
AWS Textract as a solution
The solution involves using AWS Textract for its OCR and machine learning capabilities to extract text, coupled with OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models for summarizing and parsing content to extract specific information, such as names or financial data.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- How AWS Textract differentiates from other OCR tools in handling unstructured PDF content.
- The application of OpenAI’s language models in summarizing and extracting data from text.
- The limitations of current technology in understanding complex visual and spatial elements in documents.
- The need for further development in integrating geometric data with language models for more accurate interpretation.
Pair testing: Programmers and QA working together
This use case discusses the enhancement of software quality through the collaboration of programmers and QA personnel in pair testing.
The problem: lack of communication leading to inefficiency
The piece addresses the inefficiency and lack of communication that can arise when developers and QA testers work in isolation, potentially leading to misunderstandings and a greater number of defects.
Pair testing as a solution
The solution advocated is pair testing, a technique where a programmer and a QA team member work together to test software, combining their perspectives to identify and resolve defects early in the development cycle.

From this use case, you’ll learn:
- The concept and implementation of pair testing in a development environment.
- Benefits of integrating the developers’ and QA testers’ skill sets.
- Practical insights into improving software quality and project communication.
- Strategies for fostering a collaborative culture within tech teams.
tRPC vs GraphQL – Why tRPC finally fixes the type safety hassle
This use case compares tRPC and GraphQL, highlighting tRPC as an effective solution for resolving type safety issues in web development.
The problem: Type safety with GraphQL
The problem addressed is the difficulty of achieving type safety in web development, which has been especially problematic with GraphQL, prompting the need for a better solution.
tRPC as a solution
tRPC is introduced as a TypeScript-oriented solution that integrates backend types directly with the web client, automating type generation and reducing manual coding and configuration hassles, thus streamlining the development process.
From this use case, you’ll learn:
- The intrinsic benefits of tRPC for TypeScript developers.
- How tRPC reduces effort and complexity in managing types.
- Practical steps for setting up both tRPC and GraphQL in a demo project.
- The flexibility and efficiency gains when using tRPC for frequent changes.
- The comparison of tRPC and GraphQL in terms of ease of maintenance and adaptability.
Grow faster with a dedicated team of software engineers.
BRAINHUB
TECHNOLOGİES
INSIGHTS